What are some of the key nutrients found in broccoli and how do they benefit our health?
Broccoli is an excellent source of many important nutrients that can benefit our health in several ways. Here are some key nutrients found in broccoli and their potential health benefits:
-
Vitamin C: Broccoli is a rich source of vitamin C, an antioxidant that can help to protect our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Vitamin C also supports our immune system and may help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
-
Fiber: Broccoli is high in fiber, which can promote healthy digestion, help to regulate blood sugar levels, and keep us feeling full for longer.
-
Vitamin K: Broccoli is a good source of vitamin K, a nutrient that is important for blood clotting and bone health.
-
Folate: Broccoli contains folate, a B-vitamin that is essential for healthy cell growth and development, particularly during pregnancy.
-
Potassium: Broccoli is a good source of potassium, a mineral that is important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and kidney function.
-
Calcium: Broccoli contains calcium, a mineral that is essential for strong bones and teeth.
-
Sulforaphane: Broccoli contains sulforaphane, a plant compound that has been shown to have anti-cancer properties and may help to reduce inflammation in the body.
Overall, regular consumption of broccoli can help to support our overall health and may reduce the risk of several chronic diseases.
Can eating broccoli regularly help to prevent certain types of cancer?
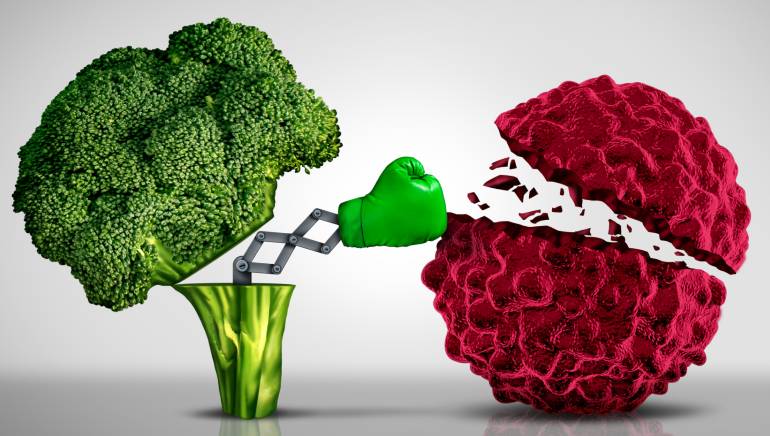

Yes, eating broccoli regularly has been linked to a reduced risk of certain types of cancer. Broccoli is a member of the cruciferous vegetable family, which also includes cauliflower, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts, and it contains several compounds that may have anti-cancer properties.
One of these compounds is sulforaphane, which has been shown to have a protective effect against several types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer. Sulforaphane works by activating enzymes in the body that can help to eliminate cancer-causing substances and prevent tumor growth.
In addition to sulforaphane, broccoli also contains other compounds that may help to reduce the risk of cancer, such as indole-3-carbinol, which has been shown to have anti-tumor effects in animal studies.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between broccoli consumption and cancer prevention, several studies have suggested that including broccoli in our diet may help to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer. However, it's important to note that broccoli should be part of a balanced and varied diet, and that other lifestyle factors, such as exercise and avoiding tobacco, also play an important role in cancer prevention.
How does broccoli support our immune system and help to fight off disease?
Broccoli can support our immune system and help to fight off disease in several ways:
-
Vitamin C: Broccoli is a rich source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that can help to boost our immune system and protect our cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals.
-
Glucosinolates: Broccoli contains compounds called glucosinolates, which are broken down into active compounds like sulforaphane when we eat them. These compounds have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties, and may also help to boost our immune system.
-
Fiber: Broccoli is high in fiber, which can help to promote healthy digestion and feed the beneficial bacteria in our gut, which play an important role in supporting our immune system.
-
Immune-boosting nutrients: Broccoli also contains several other nutrients that are important for a healthy immune system, such as vitamin E, vitamin A, and zinc.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties: Chronic inflammation has been linked to several diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Broccoli contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may help to protect against these diseases.
Overall, including broccoli in our diet can help to support our immune system and protect us against disease by providing us with a range of beneficial nutrients and compounds.
Are there any potential side effects or risks associated with eating too much broccoli?
While broccoli is generally considered to be a safe and nutritious food, eating too much of it can have some potential side effects and risks:
-
Digestive issues: Eating large amounts of broccoli can cause digestive discomfort, such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea. This is because broccoli contains a type of carbohydrate called raffinose, which is difficult to digest and can ferment in the gut.
-
Thyroid issues: Broccoli contains goitrogens, compounds that can interfere with the function of the thyroid gland. While the levels of goitrogens in broccoli are relatively low, eating very large amounts of raw broccoli may potentially interfere with thyroid function in some people.
-
Interference with medication: Broccoli contains vitamin K, which can interfere with the blood-thinning effects of some medications, such as warfarin. People taking these medications should speak with their doctor about how much broccoli they can safely eat.
-
Allergies: Some people may have an allergy to broccoli or other cruciferous vegetables, which can cause symptoms such as itching, hives, and difficulty breathing.
It's important to note that these side effects and risks are generally associated with consuming very large amounts of broccoli, and are relatively rare. For most people, including broccoli as part of a balanced and varied diet is a healthy choice that provides a range of beneficial nutrients and health benefits.
How does cooking or processing broccoli affect its nutritional value?
Cooking or processing broccoli can affect its nutritional value in different ways:
-
Loss of vitamin C: Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that is sensitive to heat and oxygen, so cooking broccoli can lead to a significant loss of this nutrient. Steaming or microwaving broccoli for a short period of time can help to minimize vitamin C loss.
-
Changes to glucosinolate content: Glucosinolates are the compounds in broccoli that give it its characteristic flavor and potential health benefits. However, cooking or processing broccoli can cause changes to the glucosinolate content. Boiling broccoli, for example, can cause a loss of up to 90% of its glucosinolate content, while steaming or microwaving can help to preserve more of these compounds.
-
Increased availability of certain nutrients: Cooking broccoli can make certain nutrients, such as carotenoids and some minerals, more available for our bodies to absorb. For example, cooking broccoli can increase the bioavailability of beta-carotene, an antioxidant that is converted to vitamin A in the body.
-
Destruction of enzymes: Broccoli contains enzymes that can help to break down nutrients and make them more easily absorbed by our bodies. However, cooking or processing broccoli can destroy these enzymes, which may reduce the availability of certain nutrients.
Overall, how cooking or processing affects broccoli's nutritional value can vary depending on the method and duration of cooking, as well as other factors such as the freshness of the broccoli. However, in general, steaming or microwaving broccoli for a short period of time is considered to be the best way to preserve its nutritional value while also making it more palatable.
What are some creative ways to incorporate broccoli into our daily diet?
There are many creative and delicious ways to incorporate broccoli into your daily diet. Here are some ideas:
-
Roasted broccoli: Toss broccoli florets with olive oil, salt, and pepper and roast in the oven until crispy and tender.
-
Broccoli salad: Combine chopped broccoli with diced apples, dried cranberries, sunflower seeds, and a tangy dressing for a flavorful salad.
-
Broccoli soup: Puree steamed broccoli with vegetable or chicken broth, garlic, and onion for a creamy and nutritious soup.
-
Broccoli stir-fry: Stir-fry broccoli with other vegetables and a protein source, such as tofu or chicken, for a quick and easy weeknight meal.
-
Broccoli and cheese quiche: Mix steamed broccoli with eggs, cheese, and other ingredients to make a hearty and satisfying quiche.
-
Broccoli and hummus dip: Dip raw broccoli florets in hummus for a healthy and flavorful snack.
-
Broccoli and cauliflower rice: Use a food processor to finely chop raw broccoli and cauliflower and sauté in a pan with garlic and other seasonings for a low-carb alternative to rice.
-
Broccoli pesto: Combine steamed broccoli with garlic, lemon juice, parmesan cheese, and pine nuts in a food processor to make a flavorful pesto sauce for pasta or sandwiches.
-
Broccoli and feta frittata: Whisk together eggs, steamed broccoli, crumbled feta cheese, and other ingredients to make a protein-rich and tasty frittata.
-
Broccoli and chicken casserole: Mix cooked chicken with broccoli, cheese, and a creamy sauce and bake in the oven for a comforting and nutritious casserole.
Can eating broccoli help to reduce inflammation in the body?
Yes, eating broccoli can help to reduce inflammation in the body. Broccoli is a rich source of compounds called flavonoids and glucosinolates, which have anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds can help to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules in the body and promote the production of anti-inflammatory molecules.
One particular compound found in broccoli, called sulforaphane, has been shown to have strong anti-inflammatory effects. Sulforaphane can help to activate a specific protein called Nrf2, which plays a key role in regulating inflammation in the body. By activating Nrf2, sulforaphane can help to reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Several studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effects of broccoli and its components. For example, one study found that consuming broccoli sprouts, which are particularly rich in sulforaphane, led to a significant decrease in levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Another study found that consuming broccoli powder led to a reduction in inflammation in people with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the anti-inflammatory effects of broccoli, there is growing evidence to suggest that including this nutritious vegetable in your diet can help to reduce inflammation and promote overall health.