What are the main health benefits of eating tomatoes?
Tomatoes are a nutrient-dense food that offers a variety of health benefits. Some of the main health benefits of eating tomatoes include:
-
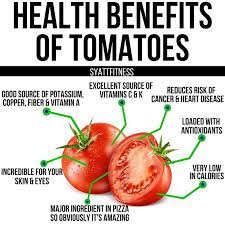
Rich in Vitamins and Minerals: Tomatoes are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as potassium and folate.
-
High in Antioxidants: Tomatoes contain high levels of the antioxidant lycopene, which has been linked to a reduced risk of certain cancers and heart disease.
-
May Reduce Risk of Heart Disease: The potassium in tomatoes can help lower blood pressure, and the antioxidants in tomatoes may help reduce inflammation, both of which are risk factors for heart disease.
-
May Improve Eye Health: The vitamin A in tomatoes is important for maintaining healthy vision, and the lycopene in tomatoes has been linked to a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration.
-
May Reduce Risk of Cancer: Lycopene and other antioxidants in tomatoes may help protect against certain types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancer.
-
May Benefit Skin Health: The vitamin C in tomatoes is important for collagen production, which is essential for healthy skin. Additionally, the lycopene in tomatoes may help protect against UV damage.
Overall, consuming tomatoes as part of a healthy diet can help promote overall health and reduce the risk of certain diseases.
How do tomatoes contribute to a healthy diet?
Tomatoes are a nutrient-dense food that can contribute to a healthy diet in several ways:
-
Low in Calories: Tomatoes are low in calories, with just 22 calories per 100 grams. This makes them a great choice for people who are watching their calorie intake.
-
High in Nutrients: Tomatoes are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, and folate. They also contain antioxidants like lycopene, which has been linked to numerous health benefits.
-
Source of Fiber: Tomatoes are a good source of dietary fiber, which is important for maintaining digestive health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
-
Versatile: Tomatoes are a versatile food that can be used in a variety of dishes, making it easy to incorporate them into a healthy diet.
-
Can Help Reduce Sodium Intake: Tomatoes are naturally low in sodium, which makes them a great alternative to high-sodium processed foods.
Overall, incorporating tomatoes into a healthy diet can help ensure that you're getting a variety of essential nutrients while keeping calories and sodium intake in check.
Can eating tomatoes help prevent certain types of cancer?

Yes, there is some evidence to suggest that eating tomatoes may help prevent certain types of cancer. Tomatoes contain a powerful antioxidant called lycopene, which gives them their bright red color. Lycopene has been shown to have anticancer properties, and several studies have suggested that consuming tomatoes or lycopene supplements may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancer.
Additionally, tomatoes are a good source of vitamin C, which is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage DNA and other cellular structures, leading to cancer and other diseases.
However, it's important to note that while there is some evidence to suggest that eating tomatoes may help prevent cancer, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between tomatoes and cancer prevention. It's also important to maintain a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases.
How do the antioxidants in tomatoes benefit our health?
The antioxidants in tomatoes can benefit our health in several ways:
-
Reduce Inflammation: Antioxidants, such as lycopene, in tomatoes can help reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is associated with several chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
-
Protect Cells: Antioxidants protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage DNA, proteins, and other cellular structures, leading to chronic diseases and premature aging.
-
Support Immune System: Antioxidants can support the immune system by neutralizing harmful molecules and protecting immune cells from damage.
-
Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases: Studies have shown that a diet rich in antioxidants can lower the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Overall, the antioxidants in tomatoes can benefit our health by reducing inflammation, protecting cells, supporting the immune system, and lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
Are there any nutrients in tomatoes that are particularly beneficial for the body?
Yes, tomatoes are rich in several nutrients that are particularly beneficial for the body, including:
-
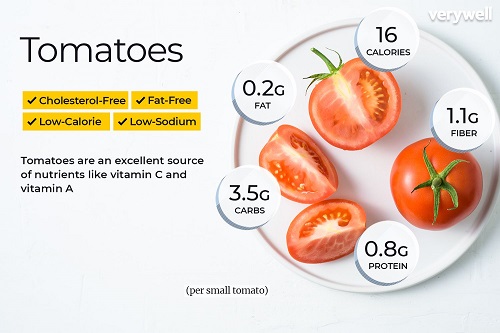
Vitamin C: Tomatoes are a good source of vitamin C, an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage, supports the immune system, and aids in the absorption of iron.
-
Vitamin K: Tomatoes are also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for blood clotting and bone health.
-
Potassium: Tomatoes are a good source of potassium, a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure, supports heart health, and aids in muscle and nerve function.
-
Lycopene: Tomatoes are a rich source of lycopene, an antioxidant that has been linked to a lower risk of certain types of cancer, as well as heart disease and stroke.
-
Fiber: Tomatoes are a good source of fiber, which can help promote digestion, regulate blood sugar levels, and support heart health.
Overall, the combination of these nutrients makes tomatoes a nutritious and healthy food choice.
How do tomatoes help with cardiovascular health?
Tomatoes can help improve cardiovascular health in several ways:
-
Lowering Blood Pressure: Tomatoes are a good source of potassium, a mineral that can help lower blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium in the diet.
-
Reducing Inflammation: Tomatoes contain antioxidants such as lycopene, which can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
-
Improving Cholesterol Levels: The fiber and antioxidants in tomatoes can help improve cholesterol levels by reducing the amount of LDL ("bad") cholesterol in the blood.
-
Preventing Blood Clots: Some studies suggest that the nutrients in tomatoes can help prevent blood clots, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Overall, regular consumption of tomatoes can contribute to better cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure, reducing inflammation, improving cholesterol levels, and preventing blood clots.
Can eating tomatoes help improve skin health?
Yes, eating tomatoes can help improve skin health in several ways:
-
Protecting Against Sun Damage: Tomatoes contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that can help protect skin from sun damage. Lycopene has been shown to reduce the damage caused by UV rays and may help prevent the formation of wrinkles and age spots.
-
Boosting Collagen Production: Tomatoes are a good source of vitamin C, which is essential for the production of collagen, a protein that helps keep skin firm and elastic. Eating tomatoes can help boost collagen production, which may help prevent sagging and wrinkles.
-
Fighting Acne: Tomatoes contain salicylic acid, which is a common ingredient in acne-fighting skincare products. Eating tomatoes may help reduce inflammation and breakouts by unclogging pores and reducing the production of sebum.
-
Moisturizing Skin: Tomatoes are high in water content, which can help hydrate and moisturize the skin from within. Eating tomatoes can help improve skin's overall hydration, which may improve its appearance and texture.
Overall, consuming tomatoes as part of a healthy and balanced diet can help improve skin health and protect against sun damage, boost collagen production, fight acne, and moisturize the skin.
What are the benefits of consuming cooked tomatoes versus raw tomatoes?
The benefits of consuming cooked tomatoes versus raw tomatoes can vary depending on the specific nutrients and compounds in the tomato and the cooking method used. Here are a few key points to consider:
-
Lycopene Absorption: Cooking tomatoes can actually increase the bioavailability of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that is more easily absorbed by the body when tomatoes are cooked. This is because the heat breaks down the cell walls of the tomato, making the lycopene more available for absorption.
-
Vitamin C and Antioxidant Loss: On the other hand, cooking tomatoes can also lead to some nutrient loss. For example, vitamin C, another important antioxidant found in tomatoes, is sensitive to heat and can be partially destroyed during cooking. Other antioxidants found in tomatoes may also be reduced during cooking, depending on the cooking method and duration.
-
Flavor and Texture: Cooking tomatoes can change their flavor and texture, making them softer and sweeter. This can make them more versatile for cooking and incorporating into different dishes.
-
Cooking Methods: The specific cooking method used can also impact the nutritional profile of cooked tomatoes. For example, roasting or grilling tomatoes can lead to greater nutrient loss than steaming or simmering them.
Overall, both raw and cooked tomatoes can provide important nutrients and health benefits, and incorporating both into your diet can help you maximize their benefits.
How many servings of tomatoes should we aim to consume per day?
There is no specific recommended daily intake of tomatoes or a set number of servings that everyone should aim for. However, incorporating tomatoes into your diet on a regular basis can provide a variety of health benefits. The American Heart Association recommends a diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, including tomatoes, as part of a healthy eating pattern. Aim to incorporate tomatoes into your meals and snacks throughout the day, such as adding fresh tomato slices to sandwiches or salads, using canned tomatoes in pasta sauce, or snacking on cherry tomatoes. It's always a good idea to speak with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best diet and nutrition plan for your individual needs.
Are there any potential side effects or risks of consuming too many tomatoes?
While tomatoes are generally safe to eat and have many health benefits, consuming too many tomatoes can potentially cause some negative effects for some individuals.
Tomatoes are high in histamines, which can cause an allergic reaction in some people. Individuals with a tomato allergy or sensitivity should avoid consuming tomatoes.
Tomatoes are also high in oxalates, which can lead to kidney stones in some people, especially those who are prone to developing them.
Eating large amounts of tomatoes or tomato-based products, such as tomato juice, sauce, or paste, can also cause acid reflux or heartburn in some individuals.
In addition, tomatoes are a part of the nightshade family of plants, which may trigger inflammation or digestive issues in some people with autoimmune conditions or certain digestive disorders.
If you have any concerns about consuming tomatoes, it's always a good idea to speak with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best diet and nutrition plan for your individual needs.