What Exactly Is FOB? FOB (free on board) is an international trade term (Incoterm) that means "free on board" or "freight on board." FOB helps to determine when the seller's liability, risks, costs, and ownership of goods pass to the buyer. It determines two critical aspects:
1) At what physical point does ownership of goods pass, and
2) Who is responsible for transportation costs and fees? The term "free on board" (FOB) refers to whether the seller or buyer is responsible for goods that are damaged or destroyed during shipping.
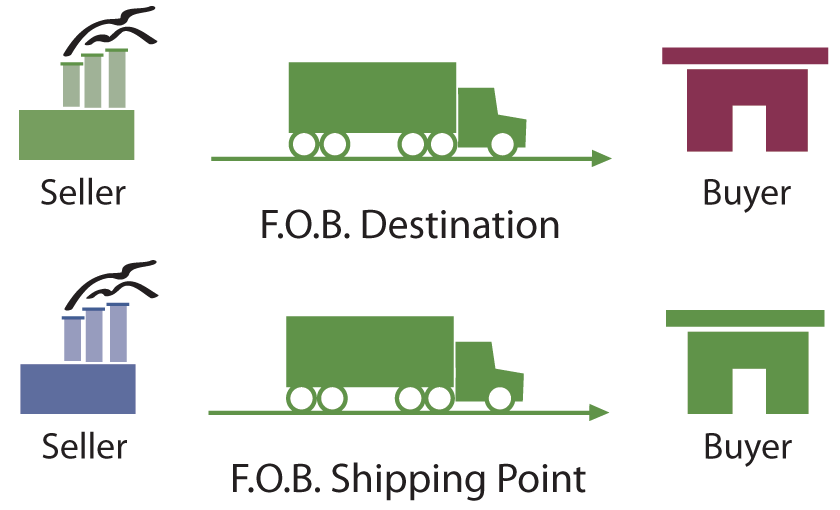
How FOB works
"FOB destination" means that the seller bears the risk of loss until the goods are delivered to the buyer.
FOB: Free on board.
FOB can be obtained in four ways:
• FOB Origin, Freight Prepaid
• FOB Destination, Freight Collect
• FOB Destination, Freight Prepaid
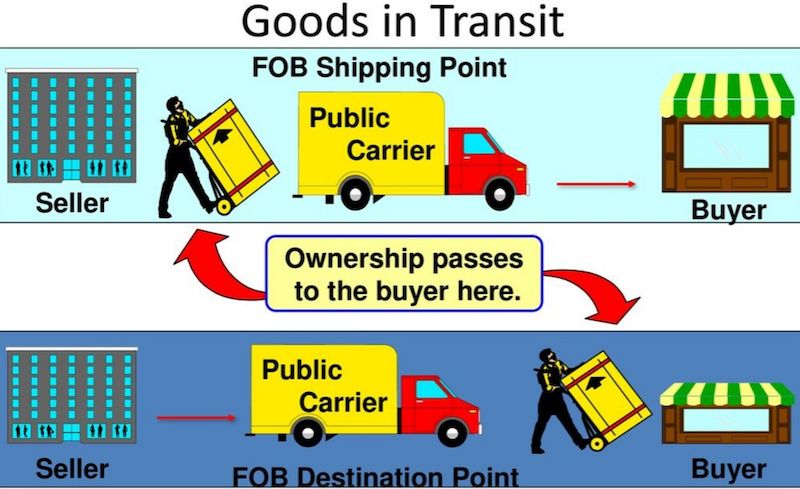
Wwnership transfer point determination is important when shipping goods - Source: www.mheducation.com
Why is it king when it comes to shipping agricultural commodities?
When you ship FOB, you have complete control over your freight costs. You have the option of hiring your own forwarder at an agreed-upon freight rate, in addition to other charges. You will also be able to obtain precise and timely information from your forwarder, resolving any service issues or hassles that may arise during transit.
FOB is typically the less expensive option for buyers and importers. Although FOB buyers must pay freight, insurance, and unloading costs, this is usually less expensive than having to pay seller fees for other types of ownership transfer agreements, such as CIF. FOB is a more competitive freight rate in general.
Furthermore,
FOB Origin gives the buyer more power. Buyers can select their own freight forwarder, giving them greater access to information about their freight transport and timeline. They can also track their packages more easily and handle their own disputes with customs or freight carriers.
Sellers like FOB because they don't have to deal with as many shipping issues. The sellers accept no responsibility if the items are damaged or lost during transit. The buyers must handle all claims and damages, as well as bear all associated costs.
It should be noted that a freight hauler or shipping company is still liable for any damage that occurs during transit. In the case of FOB Origin, however, the carrier would only work with the buyer and the buyer's insurance to resolve any claims or disputes.
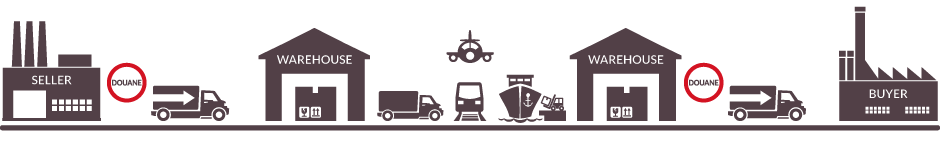
How FOB works - Source: redwoodlogistics.com
FOB is frequently recommended for buyers because it provides greater control at a lower cost. In most FOB cases, the process goes as follows:
• The seller loads the good onto the freight vessel of the buyer's choice.
• The seller clears goods for export in their country.
• The freight hauler picks up and signs for the package, at which point title to the goods passes to the buyer.
• The buyer is then responsible for insurance costs and risks associated with freight transport for the remainder of the transit.
Cotton,
corn,
citrus
fruits,
non citrus fruits,
maize,
rice,
other agricultural products
are shipped by FOB.
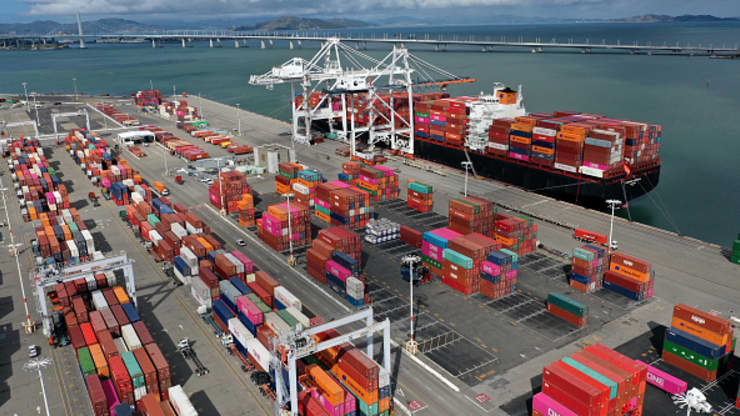

Drone footage shows shipping containers on a port at the Port of Oakland on March 9, 2021 in Oakland, California. - Source: cnbc.com


